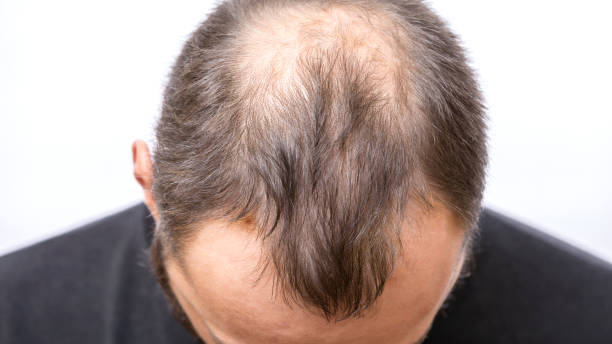
Preface Hair loss is a common condition that affects numerous individualities, both men and women, at some point in their lives. Whether it’s a retreating hairline, lacing hair, or bald spots, can have a significant impact on tone- regard and overall good.
Understanding the causes of hair loss is pivotal for effective forestallment and treatment. In this composition, we will explore the main causes of hair loss, including genetics, hormonal changes, medical conditions, and environmental factors. By the end of this composition, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of the factors that contribute to hair loss, and how to take precautionary measures to maintain healthy hair.
1.Genetics:
Genetics plays a significant part in hair loss, and it’s frequently the primary factor that determines whether an existent will witness hair loss in their continuance. Hereditary also known as androgenetic alopecia, is the most common form of and is caused by a inheritable perceptivity to dihydrotestosterone( DHT), a hormone that shrinks hair follicles.
manly pattern baldness is the most well- known form of heritable affecting about 50 of men over the age of 50. This condition generally presents as a retreating hairline and balding at the crown of the head. Womanish pattern baldness is less common, affecting around 40 of women over the age of 50, and generally presents as thinning of hair on the top of the head.
exploration shows that inheritable factors are responsible for over to 80 of cases of heritable hair loss. If a person has a family history of they’re more likely to witness it themselves. Studies have also linked specific genes that are associated with, including the AR gene, which is responsible for rendering the androgen receptor, and the PAX1 gene, which is involved in hair follicle development.
Understanding the inheritable element of is pivotal for those who want to take precautionary measures to cover their hair health. While genetics can not be changed, there are several treatments available to decelerate or indeed reverse including specifics like minoxidil and finasteride, hair transplant surgery, and low- position ray remedy.
2. Hormonal Changes:
Hormonal changes and their part in hair loss Hair loss during gestation and menopause Polycystic Ovary Pattern( PCOS) and its impact on hair health Hormones play a pivotal part in regulating hair growth, and any oscillations can lead to hair loss. During gestation, hormonal changes can beget an increase in hair growth.
still, after delivery, the hormonal balance shifts, and can do. Also, during menopause, the drop in estrogen situations can affect in hair loss. Polycystic Ovary Pattern( PCOS) is a hormonal complaint that can beget in women, among other symptoms. Women with PCOS have advanced situations of androgen, a manly hormone, which can lead to on the crown. Understanding the impact of hormonal changes on hair health can help individualities identify the cause of their and seek applicable treatment.
3. Medical Conditions:
Hair loss can be caused by colorful medical conditions, similar as thyroid problems, autoimmune diseases, and crown infections. When the thyroid gland is hyperactive or underactive, it can disrupt the hair growth cycle and beget hair loss. Autoimmune diseases similar as alopecia aerate can beget by attacking hair follicles.
Crown infections like ringworm can also lead to if left undressed. Specifics similar as chemotherapy medicines, antidepressants, and blood thinners can also beget as a side effect. It’s important to speak with a healthcare professional if you suspect that a medical condition may be causing your. They can help diagnose and treat the beginning condition, which can ameliorate your hair health.
4. Environmental Factors:
Hair follicles can be damaged by exposure to colorful environmental factors, including adulterants, poisons, and ultraviolet radiation from the sun. Also, certain hair styling products, similar as those containing harsh chemicals or alcohol, can damage the hair and lead to hair loss.
5. Exposure to adulterants and poisons:
Exposure to adulterants and poisons can damage follicles and contribute to hair loss. Air pollution, similar as from auto exhaust or artificial emigrations, can beget oxidative stress on the and crown, leading to damage and hair loss. Also, exposure to poisons in water, food, or other environmental sources can also affect hair health.
Impact of hair styling products and treatments Harsh chemicals and high heat can damage t shaft and beget breakage, leading to thinning and over time. It’s important to use hair products hair and treatments in temperance and to avoid those that are too harsh for your hair type.
6. Prevention and Treatment:
Precautionary measures can help reduce the threat of hair loss. A balanced diet with plenitude of protein and vitamins can promote healthy hair growth, while avoiding tight hairstyles can help reduce hair breakage and damage. If you’re passing seeking professional help is recommended.
Treatment options include drug, similar as topical or oral treatments, and hair transplant surgery. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the stylish treatment plan for your individual requirements.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, hair loss is a common and frequently distressing condition that can affect individualities of all periods and genders. In this composition, we’ve explored the main causes of including genetics, hormonal changes, medical conditions, and environmental factors. It’s important to understand these causes and take precautionary measures to maintain healthy hair.
Still, if you’re passing it’s always stylish to seek professional help from a good healthcare provider or a dermatologist. They can help diagnose the underpinning cause of your and recommend the stylish treatment options for your specific situation. Flash back, healthy hair isn’t just a matter of aesthetics, it can also impact your overall good. By taking care of your hair and understanding the causes of hair loss, you can promote a healthy and confident life.